Learn extra at:
Each new protocol introduces its personal complexities. When a brand new protocol exhibits up, the primary query to ask is whether or not it’s really vital. So, let’s ask that query in regards to the model context protocol (MCP).
The present wave of agentic apps, sparked by instruments like ChatGPT, are powered by large language models (LLMs) that excel at duties like summarization, content material creation, and picture processing however include elementary limitations. Particularly:
- No entry to real-time knowledge
- No entry to non-public knowledge
- No means to execute instruments
MCP addresses the above limitations by appearing as a common protocol that connects agentic apps to real-world knowledge and instruments. Nevertheless it’s honest to ask, why introduce a brand new protocol once we have already got safe and high-performing APIs?
The brief reply is that, whereas at this time’s highly effective APIs will be linked to agentic apps, there’s a problem. These APIs range broadly, e.g. REST, GraphQL, gRPC, utilizing HTTP, WebSockets, Pub/Sub. Their auth mechanisms differ too, e.g. API keys, OAuth2. Which means every integration is bespoke. Builders should learn docs, construct flows, and wire up APIs one after the other.
WSO2
This static integration mannequin is confirmed however doesn’t match the dynamic nature of agentic apps. That’s the place MCP is available in. MCP defines clear client-server roles, a normal protocol format, and a life cycle, primarily turning into the common connector between LLMs and exterior techniques. So you’ll be able to consider MCP because the USB-C within the API world.
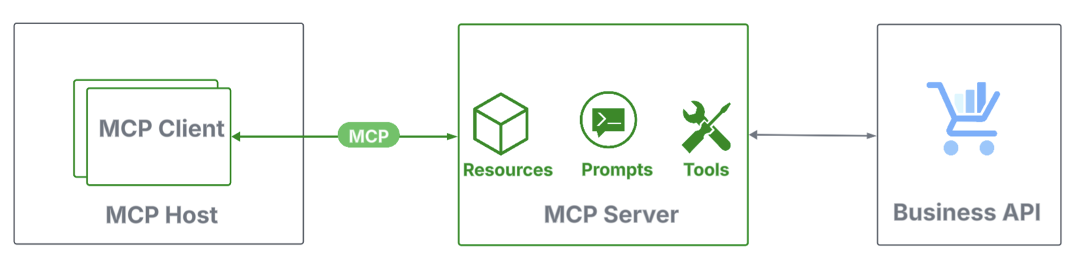
How MCP works
MCP defines three core roles—a bunch, a shopper, and a server:
- Host: Agentic functions that handle shopper life cycles and implement safety.
- Shopper: Light-weight connectors inside hosts that set up a 1:1 session with an MCP server.
- Server: Packages that join MCP shoppers to knowledge sources and instruments, both domestically or remotely.
WSO2
Every function gives a set of options. MCP servers expose assets (contextual knowledge like calendar occasions), prompts (structured templates that information person enter to enhance LLM output), and instruments (executable features). MCP shoppers connect with MCP servers to request knowledge, execute instruments, and orchestrate brokers.
MCP makes use of JSON-RPC, a light-weight, structured protocol for requests and responses, and defines two customary transport mechanisms for client-server communication, customary enter and output (STDIO) and streamable HTTP.
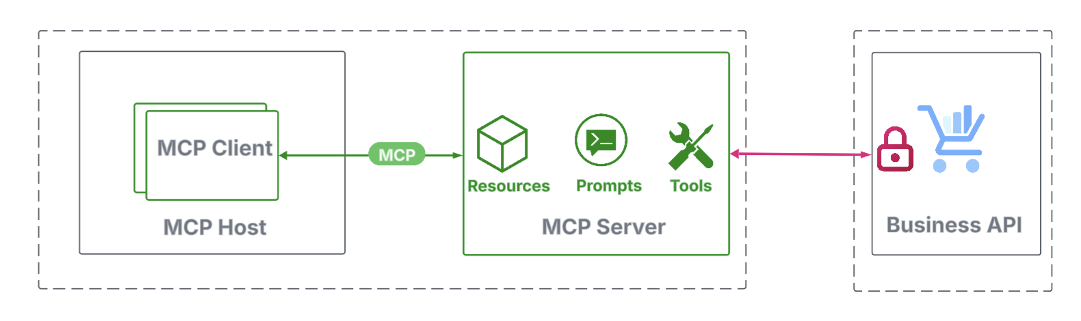
Securing an area MCP server
When the MCP server runs domestically, the STDIO transport needs to be used. In observe, this implies the agentic app launches the MCP server as a sub-process and communicates via its customary enter and output streams. As a result of this communication stays completely throughout the native system, it’s inherently safe, and the MCP auth spec doesn’t require any further safety.
WSO2
Nonetheless, when an MCP server communicates with back-end APIs, usually over the web, safety turns into a prime precedence, however falls outdoors the scope of the MCP auth specification. However, there may be nonetheless no want for brand spanking new mechanisms; current API safety practices suffice. Widespread approaches embrace:
- Lengthy-lived tokens: API keys and tokens, legitimate for days or months, are obtained by way of out-of-band channels and configured within the MCP server.
- Brief-lived tokens: With lifespans underneath an hour, short-lived tokens can’t be set manually. As an alternative, the MCP server should dynamically request them at run time with person approval. OAuth2 entry tokens and JWTs are typical examples.
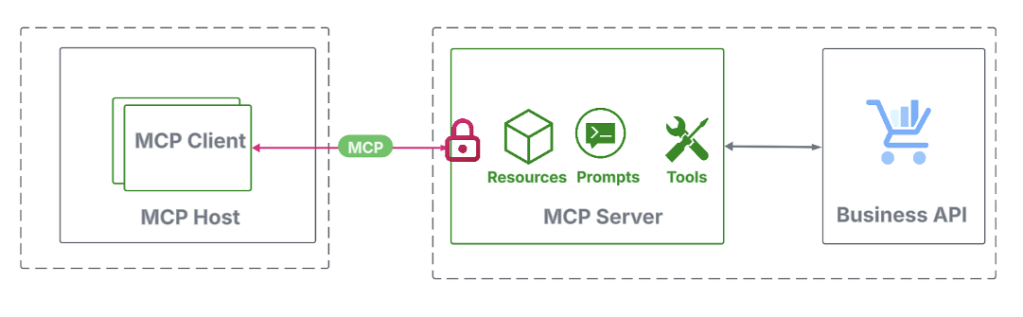
Securing a distant MCP server
An MCP shopper connects to a distant MCP server by way of HTTP by initiating a request to its endpoint URL. As specified by the MCP auth spec, this endpoint should be OAuth 2.1-protected, requiring the shopper to current a legitimate entry token.
WSO2
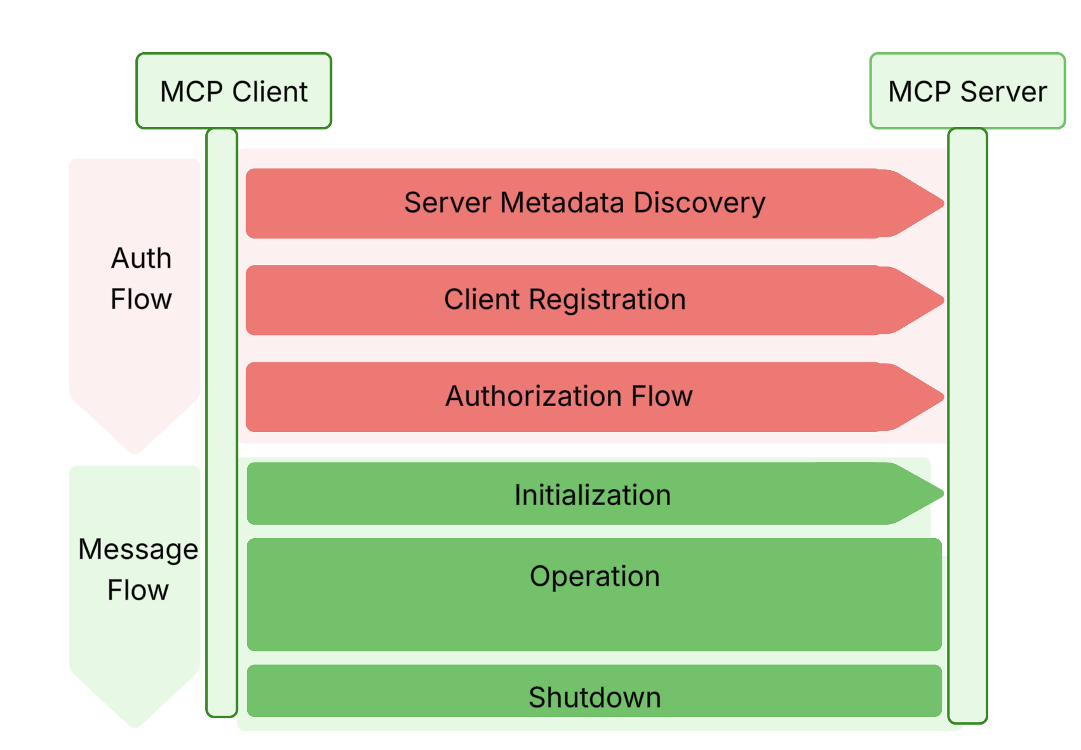
The MCP auth spec outlines a token acquisition course of designed to assist dynamic, agentic integrations. These interactions embrace the next steps.
WSO2
Server metadata discovery
As soon as the MCP server URL is supplied as a configuration parameter, the shopper constructs a server metadata endpoint by eradicating any path parts and appending a /well-known/oauth-authorization-server path. The shopper then retrieves a JSON-formatted server metadata doc from this endpoint. Each the endpoint and the doc should adjust to the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Server Metadata specification. This metadata helps the shopper uncover the next data required throughout the subsequent steps:
- Registration endpoint
- Authorization and token endpoints
- Supported grant sorts and scopes
Deriving the server metadata endpoint from the MCP server URL was meant to let shoppers function with a single configuration parameter. Nonetheless, this tightly {couples} the authorization and useful resource server roles, limiting using current OAuth 2.0 infrastructure and purpose-built id options. To handle this, the upcoming MCP auth spec replaces this mechanism with the OAuth 2.0 Protected Useful resource Metadata specification.
Shopper registration
Primarily based on the knowledge retrieved from the server metadata doc, the shopper software sends a registration request to the shopper registration endpoint. The MCP auth specification adopts the OAuth 2.0 Dynamic Shopper Registration (DCR) protocol to register the shopper as an OAuth 2.1 shopper. Within the DCR response, the shopper software receives a client_id and, for confidential shoppers, a client_secret. Each are required for the subsequent step.
Whereas DCR is broadly adopted, opinions range on open registration, and the spec itself permits defending the registration endpoint with OAuth 2.0. Once more, to assist single-parameter configuration, the MCP auth spec recommends open registration. It stays to be seen how it will evolve.
Entry token retrieval
At this stage, the shopper has the whole lot wanted to request an entry token. Relying on the use case, one of many following OAuth 2.1 grant sorts is used:
- Shopper Credentials: If the shopper software is accessing the MCP server instantly, it makes use of the Shopper Credentials grant with the
client_idandclient_secretobtained throughout registration, together with the token endpoint and scopes found from the server metadata. - Authorization Code: If the shopper accesses the MCP server on behalf of an finish person, it makes use of the Authorization Code grant. This movement requires the
client_idandclient_secretfrom registration and the authorization endpoint, token endpoint, and scopes from the server metadata. Moreover, as required by OAuth 2.1, the shopper should use Proof Key for Code Alternate (PKCE) to boost safety.
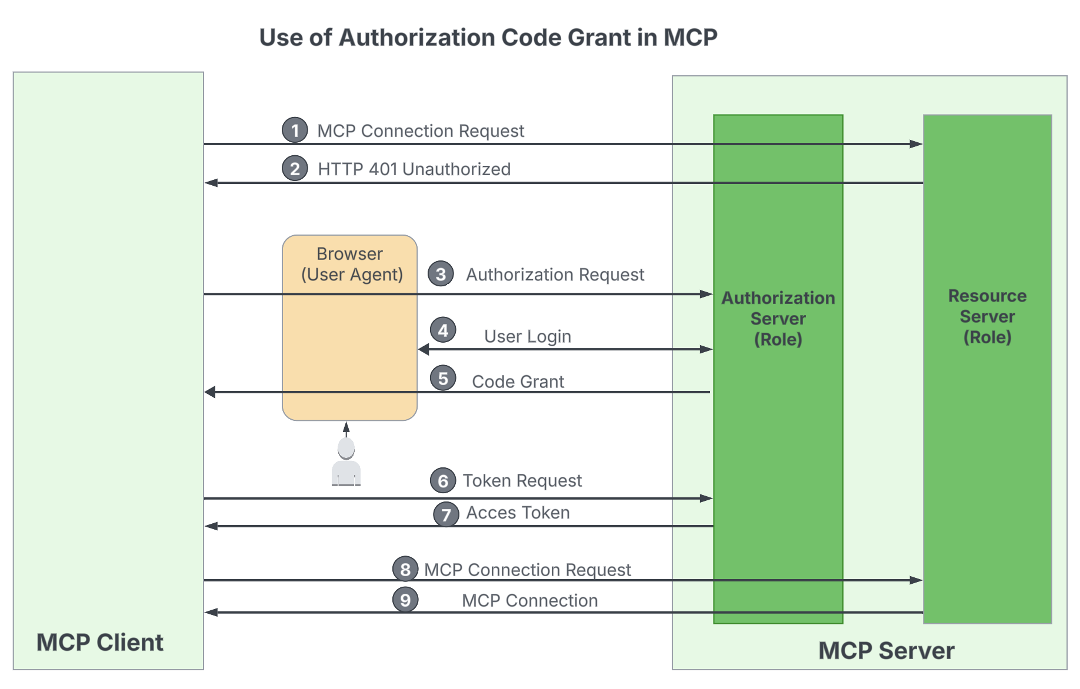
WSO2
If the whole lot goes effectively, the shopper software obtains a legitimate entry token and might provoke a connection request to the MCP server URL, passing the token by way of the Authorization HTTP header. The MCP server then validates the token and establishes the connection if it’s legitimate.
In the end, this safety movement aligns with typical OAuth-based API safety flows, aside from the preliminary step of deriving the server metadata URL from the MCP server URL.
Sagara Gunathunga is director of options structure at WSO2.
—
Generative AI Insights gives a venue for expertise leaders to discover and focus on the challenges and alternatives of generative synthetic intelligence. The choice is wide-ranging, from expertise deep dives to case research to professional opinion, but in addition subjective, primarily based on our judgment of which subjects and coverings will greatest serve InfoWorld’s technically refined viewers. InfoWorld doesn’t settle for advertising and marketing collateral for publication and reserves the proper to edit all contributed content material. Contact doug_dineley@foundryco.com.


