Learn extra at:
Why it issues: A technological leap in fiber optics has shattered earlier limitations, attaining what specialists as soon as thought-about inconceivable: transmitting information at 1.02 petabits per second – sufficient to obtain each film on Netflix 30 occasions over – throughout 1,808 kilometers utilizing a single fiber no thicker than a human hair.
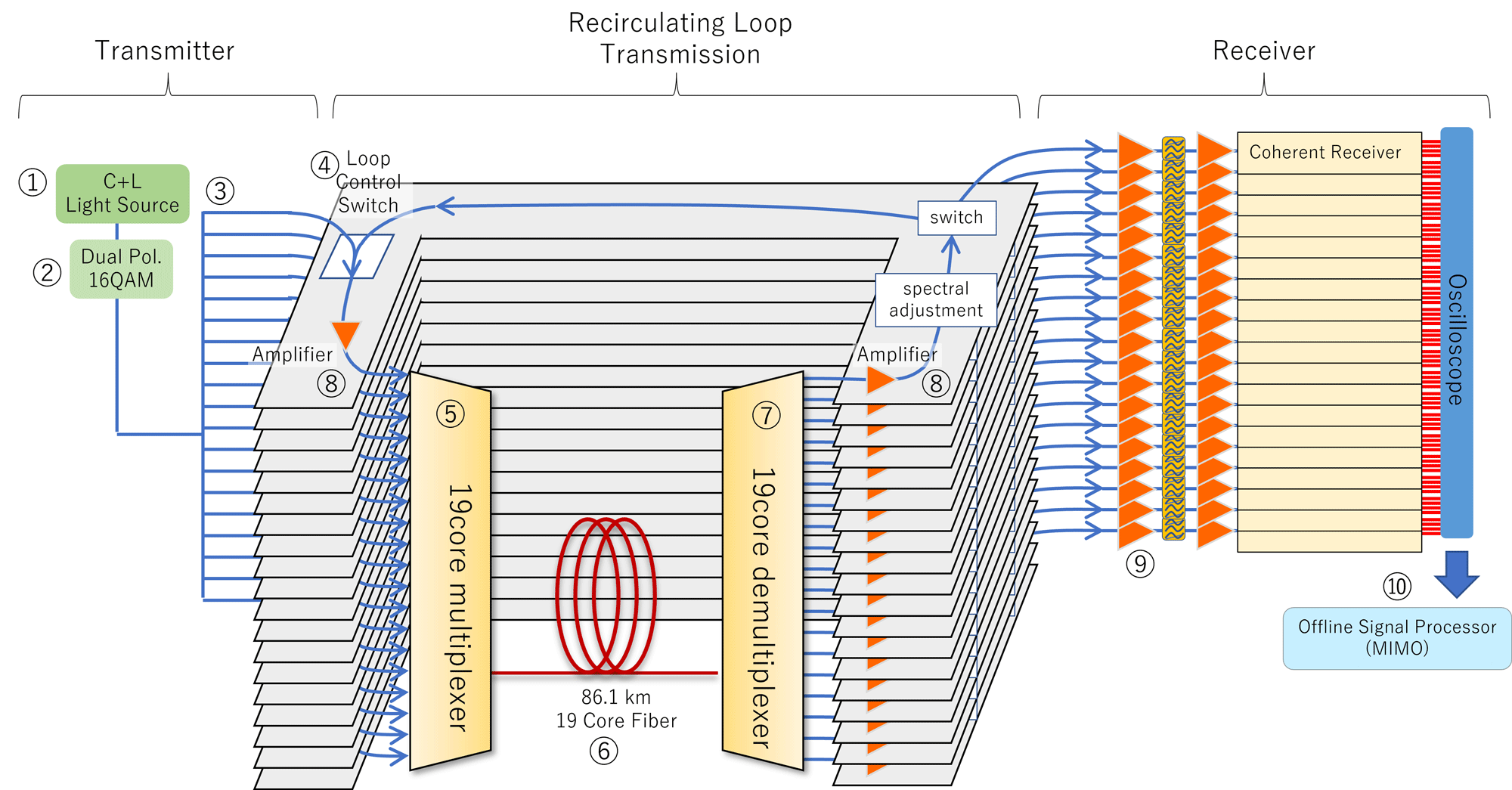
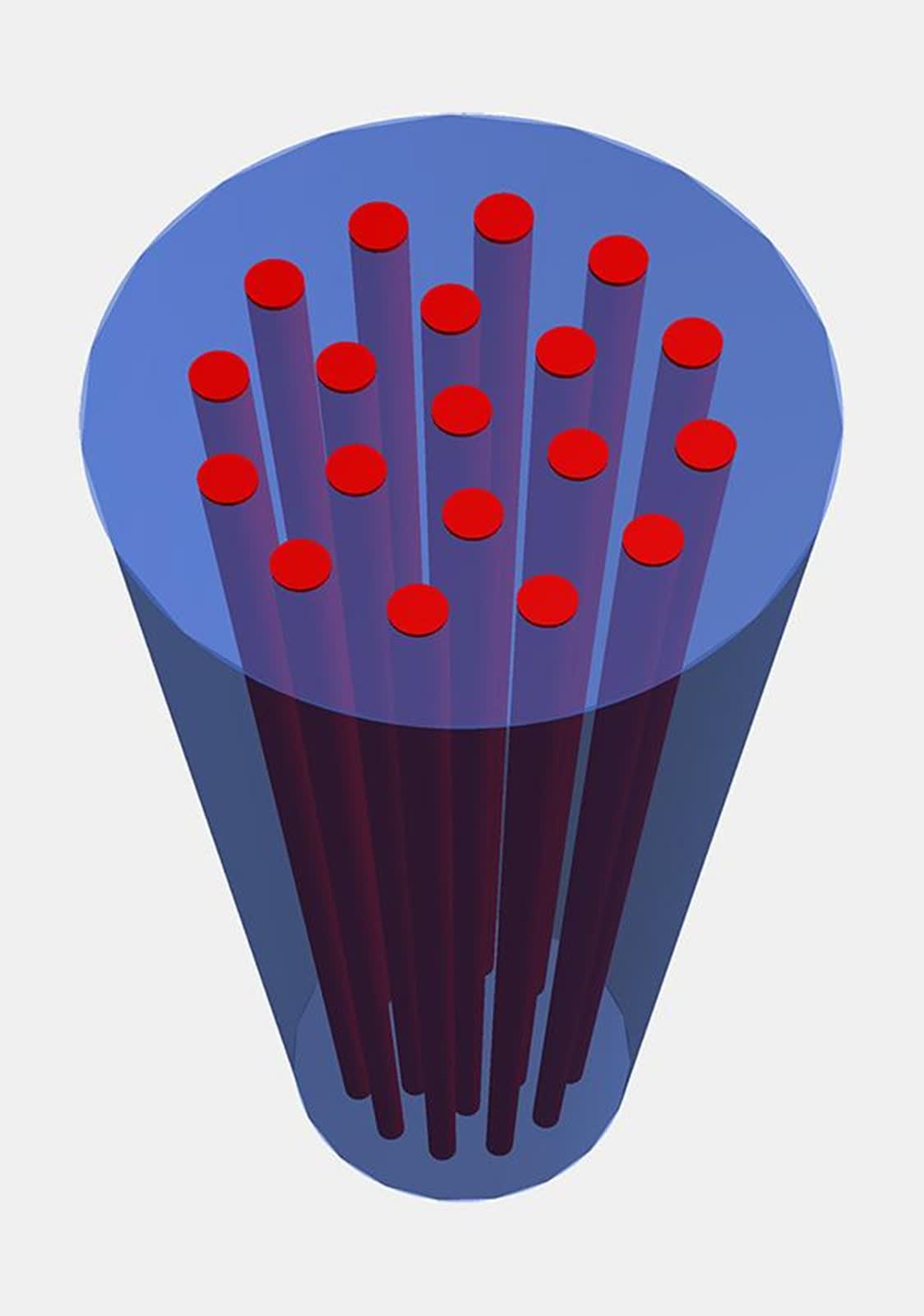
On the coronary heart of this breakthrough – pushed by Japan’s Nationwide Institute of Data and Communications Expertise (NICT) and Sumitomo Electrical Industries – is a 19-core optical fiber with a normal 0.125 mm cladding diameter, designed to suit seamlessly into present infrastructure and get rid of the necessity for pricey upgrades.
Every core acts as an impartial information channel, collectively forming a “19-lane freeway” inside the identical area as conventional single-core fibers.
Not like earlier multi-core designs restricted to brief distances or specialised wavelength bands, this fiber operates effectively throughout the C and L bands (business requirements used globally) because of a refined core association that slashes sign loss by 40% in comparison with prior fashions.
The experiment’s success relied on a posh recirculating loop system. Indicators traveled by means of an 86.1-kilometer fiber section 21 occasions, simulating a cross-continental journey equal to linking Berlin to Naples or Sapporo to Fukuoka.
To keep up integrity over this distance, researchers deployed a dual-band optical amplification system, comprising separate units that boosted alerts within the C and L bands. This enabled 180 distinct wavelengths to hold information concurrently utilizing 16QAM modulation, a technique that packs extra info into every pulse.
On the receiving finish, a 19-channel detector, paired with superior MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) processing, dissected interference between cores, very similar to untangling 19 overlapping conversations in a crowded room.
This digital sign processor, leveraging algorithms developed over a decade of multi-core analysis, extracted usable information at unprecedented charges whereas correcting for distortions collected over 1,808 km.
The achievement caps years of incremental progress. In 2023, the identical crew achieved 1.7 petabits per second, however solely throughout 63.5 km. Earlier efforts utilizing 4-core fibers reached 0.138 petabits over 12,345 km by tapping the much less sensible S-band, whereas 15-mode fibers struggled with sign distortion past 1,001 km as a result of mismatched propagation traits.
The brand new 19-core fiber’s uniform core design sidesteps these points, attaining a capacity-distance product of 1.86 exabits per second per kilometer – 14 occasions greater than earlier information for traditional fibers.
Offered because the top-rated post-deadline paper at OFC 2025 in San Francisco, this work arrives as world information visitors is projected to triple by 2030.
Whereas challenges stay, similar to optimizing amplifier effectivity and scaling MIMO processing for real-world use, the know-how provides a viable path to petabit-scale networks. Researchers purpose to refine manufacturing methods for mass deployment, probably enabling transoceanic cables that transfer total information facilities’ value of data hourly.
Researchers purpose to refine manufacturing methods for mass deployment, probably enabling transoceanic cables that transfer total information facilities’ value of data hourly.
Sumitomo Electrical’s engineers, who designed the fiber’s coupled-core structure, notice that present manufacturing strains can adapt to supply the 19-core design with minimal retooling.
In the meantime, NICT’s crew is exploring AI-driven sign processing to additional enhance speeds. As 6G and quantum computing loom, this breakthrough positions fiber optics not simply as a spine for tomorrow’s web, however because the central nervous system of a hyperconnected planetary infrastructure.