Learn extra at:
In the summertime of 2025, an enormous 8.8-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula. Whereas that isn’t one of many five largest earthquakes ever recorded, that’s nonetheless impressively highly effective. That earthquake triggered a tsunami that unfold throughout the Pacific Ocean, and NASA’s new SWOT satellite tv for pc captured the monster wave intimately.
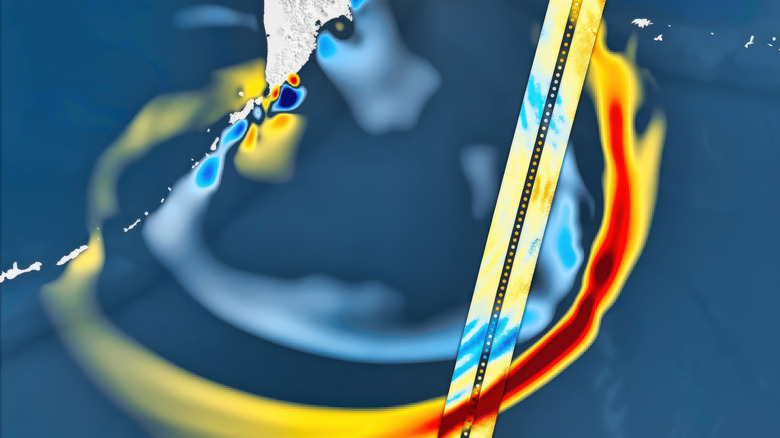
The SWOT satellite tv for pc, quick for Floor Water and Ocean Topography, solely lately launched in 2022. This earthquake is the most important the satellite tv for pc has captured up to now. Utilizing knowledge from it and deep-ocean tsunami buoys, researchers have been capable of map the earthquake’s rupture zone, which stretched roughly 250 miles and lifted elements of the seafloor by as much as 13 toes. The satellite tv for pc was capable of seize how the tsunami waves modified as they traveled, giving scientists an in-depth mannequin to be taught from.
The analysis into this occasion was printed in The Seismic Record in November 2025. The publication highlights how harmful megaquakes could be, and reveals how satellites like SWOT are remodeling scientists’ capability to know, observe, and predict tsunamis.
Particulars of how the enormous tsunami was noticed
Satellites have remodeled the way in which we examine our planet and provides us uncommon glimpses into occasions that occur within the ocean that people is probably not on sight to witness, equivalent to this record-breaking wave. To determine precisely how the 2025 Kamchatka tsunami fashioned and unfold, scientists mixed knowledge from Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) tsunami warning system and NASA’s SWOT satellite tv for pc.
The NOAA system, generally known as DART (Deep-ocean Evaluation and Reporting of Tsunamis), makes use of sensors anchored to the seafloor that may detect adjustments in water stress. It then sends that knowledge to floor buoys and satellites in virtually actual time. When the Kamchatka quake struck, a number of of those stations instantly switched into high-alert mode, capturing the tsunami because it moved away from the supply.
The analysis workforce centered on the closest sensors, filtering out regular ocean tides so they may work backward and estimate how the seafloor truly shifted through the earthquake. On the similar time, SWOT handed over the area and recorded a 75-mile-wide strip of ocean floor, capturing the tsunami’s form and movement from area in excessive decision. Processing the information allowed scientists to obviously see the tsunami’s waves and the way they unfold and dispersed regardless of how rapidly the tsunami was transferring.
What this implies for tsunami science
Earthquakes and their resulting tsunamis may be even more dangerous than we thought, and this knowledge provides key insights to assist us be taught and put together for these occasions. What made this occasion much more fascinating is that its knowledge could possibly be in comparison with a 9.0 magnitude earthquake in the very same space that occurred in 1952 that concerned the identical fault zone.
Evaluating the 2 quakes, scientists deduced that the 1952 earthquake did not launch all of the built-up stress within the fault, resulting in this newest earthquake. Since these quakes occurred so shut collectively, it challenges long-standing hazard fashions that anticipate huge earthquakes to be separated by lots of of years. Scientists have been additionally capable of analyze the place the 2 quakes occurred, with the older one being nearer to the seafloor and the newer one deeper underground, and the way that impacts the dimensions of the tsunami on the ocean floor. Although each prompted evacuations, the 2025 tsunami didn’t trigger the injury the 1952 one did.
The SWOT satellite tv for pc additionally reveals it could actually revolutionize real-world response to tsunami emergencies as it could actually present knowledge rapidly. The underwater buoy system working in tandem with the satellite tv for pc has confirmed reliability in monitoring tsunami waves. Scientists at the moment are seeking to the way forward for how this technique can work with coastal warning programs and assist the general public safely reply to large tsunamis.