Learn extra at:
The large image: AMD lastly revealed the specs, pricing, and efficiency particulars of Radeon RX 9070 and Radeon RX 9070 XT graphics playing cards, with full opinions anticipated within the coming days. Whereas we await these, we have already mentioned the potential performance implications, FSR 4 upscaling, and now we need to present extra context on enhancements within the new Radeon’s encoding high quality – an usually missed side of latest GPUs (together with by us).
AMD’s GPU encoders have lengthy been criticized for poor video encoding high quality when utilizing common codecs and bitrates for sport streaming, leaving Nvidia because the clear selection for anybody who needs to make use of video encoding.
With RDNA 4, AMD claims encoding high quality is considerably improved, and the examples they showcased had been definitely attention-grabbing. AMD is particularly highlighting 1080p H.264 and HEVC at 6 megabits per second – one of the generally used setups – demonstrating a considerable improve in visible high quality.
Whether or not this may maintain true throughout a broad number of situations stays to be seen, however traditionally, AMD’s discussions on encoding high quality have revolved round supporting new codecs like AV1. With RDNA 4, AMD is specializing in tangible enhancements in real-world use instances, suggesting they’re way more assured of their encoder’s high quality.
AMD is touting a 25% achieve in H.264 low-latency encode high quality, an 11% enchancment in HEVC, higher AV1 encoding with B-frame help, and a 30% enhance in encoding efficiency at 720p. These numbers probably check with VMAF scores.
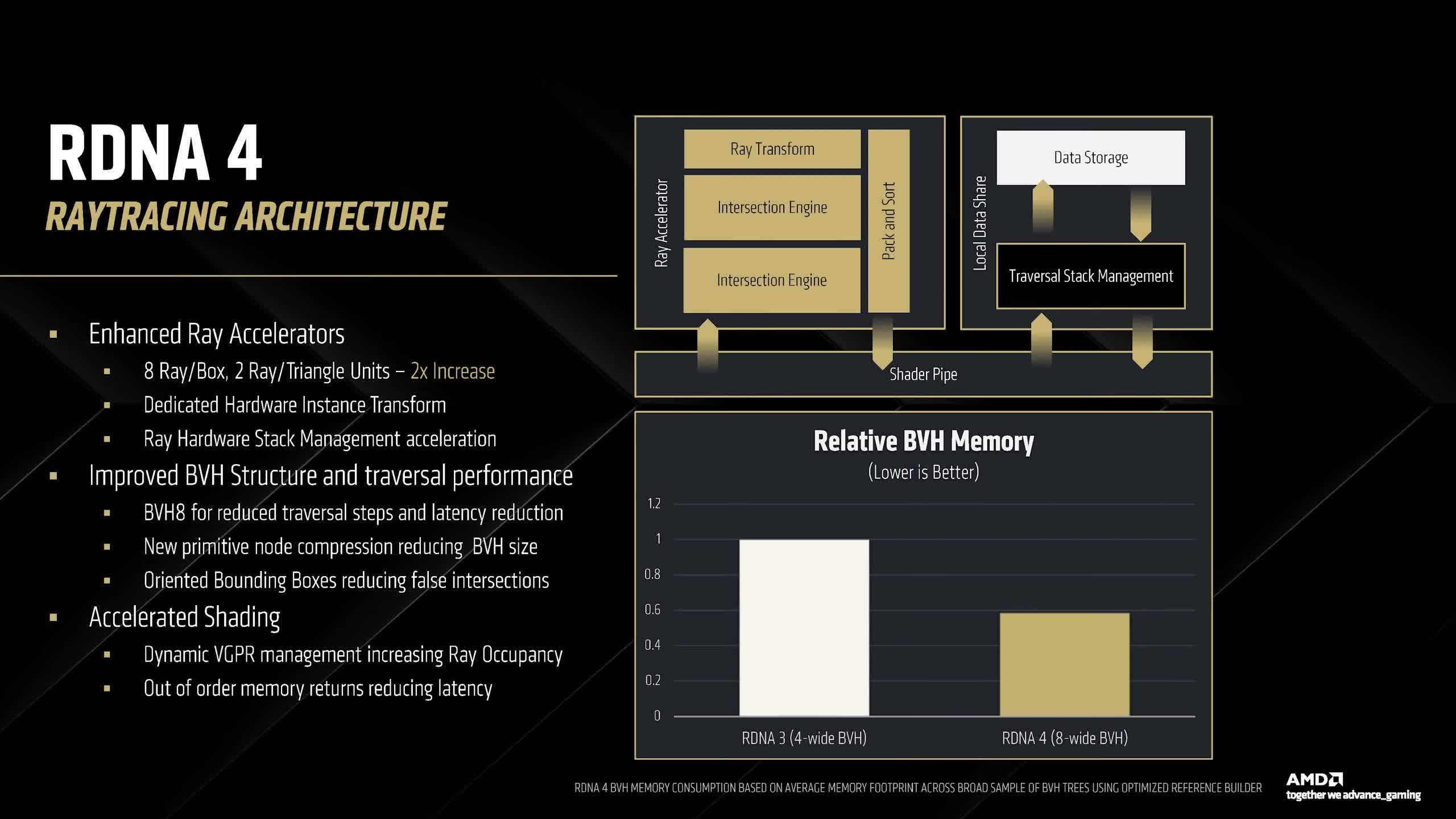
Past encoding, there are a number of different notable enhancements. The ray tracing core now options two intersection engines as a substitute of 1, doubling throughput for ray-box and ray-triangle intersections. A brand new ray remodel block has been launched, offloading sure points of ray tracing from shaders to the RT core.
The BVH (Bounding Quantity Hierarchy) is now twice as huge, and quite a few different enhancements have been made to the ray tracing implementation – one purpose why RDNA 4’s ray tracing positive aspects exceed its rasterization enhancements.
Compute, Reminiscence, and Show Enhancements
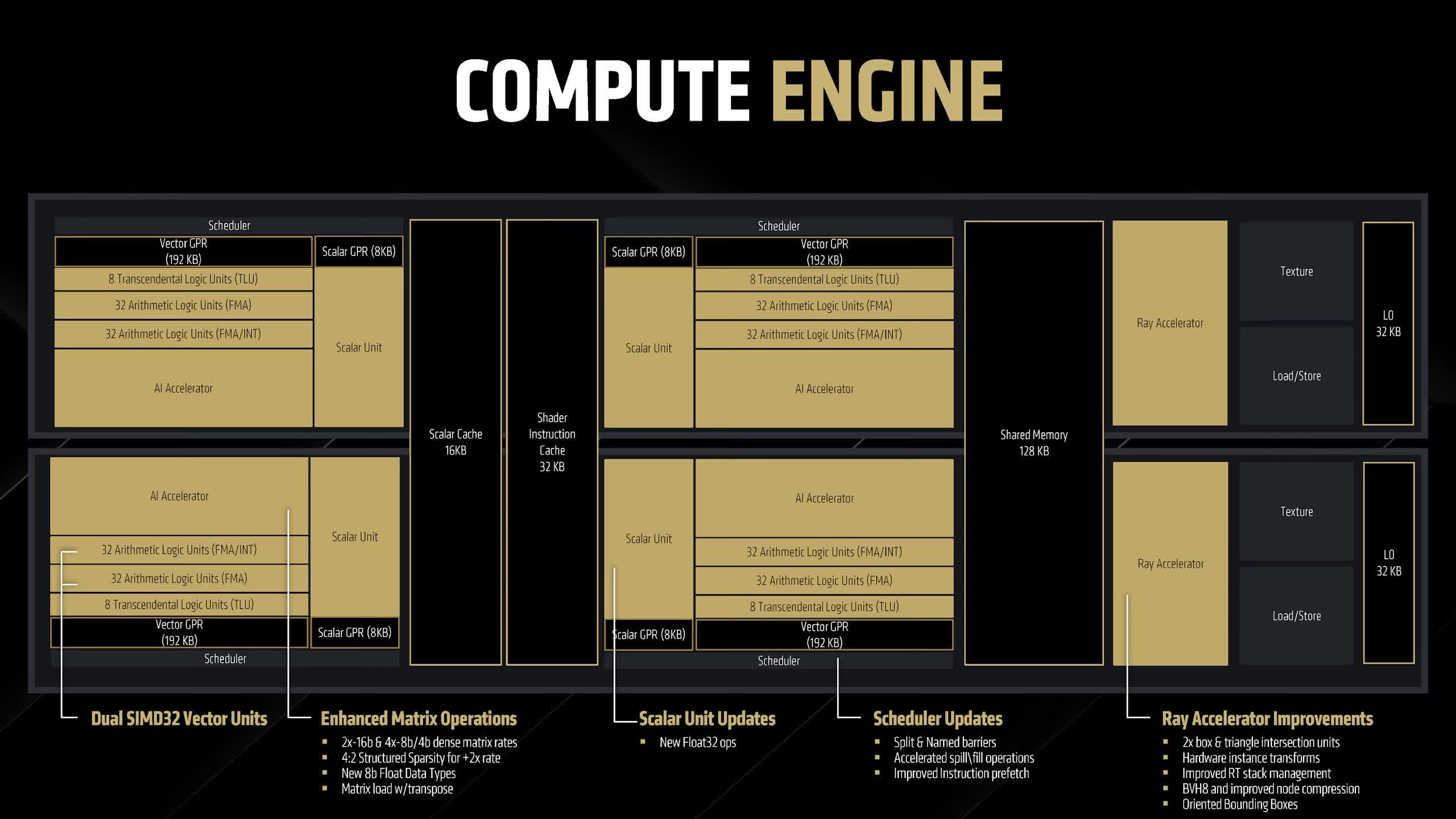
The compute engine additionally consists of a number of optimizations, together with a PCIe 5.0 x16 interface and a 256-bit reminiscence bus utilizing GDDR6. AMD claims enhanced reminiscence compression, and the GPUs are outfitted with 16GB of VRAM, which needs to be adequate for many fashionable video games.
The show engine, nonetheless, is a combined bag. Whereas it helps DisplayPort 2.1, its capabilities stay unchanged from RDNA 3, with a most bandwidth of UHBR 13.5 as a substitute of the total UHBR 20 now used on some 4K 240Hz shows and supported by Nvidia’s Blackwell structure.
HDMI 2.1b can be included. On a constructive be aware, AMD claims decrease idle energy consumption for multi-monitor setups, and video body scheduling can now be offloaded to the GPU.
The Navi 48 die is 357mm² of TSMC 4nm silicon, that includes 53.9 billion transistors. This makes it 5% smaller than Nvidia’s Blackwell GB203 used within the RTX 5080 and 5070 Ti, but it accommodates 18% extra transistors, which means the design is extra densely packed.
Nonetheless, Nvidia nonetheless holds a bonus by way of die space and transistor effectivity, because the RTX 5080 is predicted to be about 15% sooner in rasterization and presumably over 50% sooner in ray tracing based mostly on AMD’s RX 9070 XT claims – all whereas utilizing fewer transistors and a smaller die. That stated, the TDP of the RTX 5080 is 360W, in comparison with 304W for the 9070 XT, an 18% larger energy draw – although precise energy consumption in video games could fluctuate. The 9070 XT needs to be nearer to the RTX 5070 Ti with its 300W TDP.
A few extra particulars to spherical issues out: AMD is just not producing reference fashions for the RX 9070 XT or RX 9070, which means all designs will come from board companions. These companions embody ASUS, Gigabyte, PowerColor, Sapphire, XFX, and different acquainted names.
Availability is predicted to be robust on March sixth, as these playing cards have reportedly been prepared since early January.
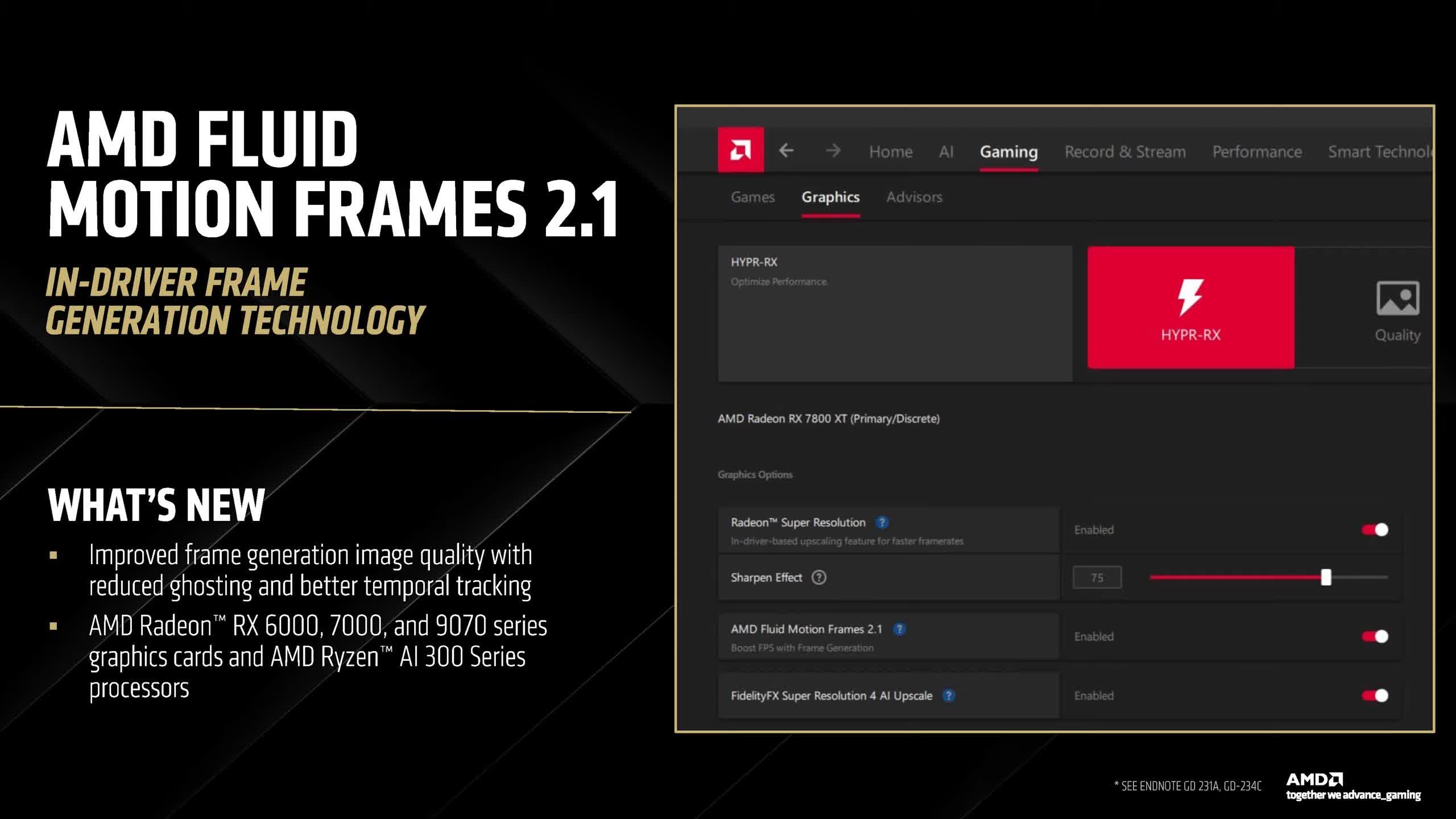
Moreover, AMD is releasing a brand new model of its driver-based body era expertise, AFMF 2.1, which might be out there for the Radeon RX 6000 collection and newer GPUs.
This model guarantees superior picture high quality and consists of Radeon Picture Sharpening, which will be utilized to any sport, video, or software on the driver stage. AMD additionally claims improved high quality for this characteristic. There are additionally some AI-related options, although nothing significantly groundbreaking.