Learn extra at:
Why it issues: As the usage of generative AI turns into more and more widespread in training, regulation, politics, media, and different fields, many fear that reliance on the know-how might cut back cognitive independence. A current research from MIT strongly helps this concern, indicating that the usage of digital instruments considerably alters mind exercise.
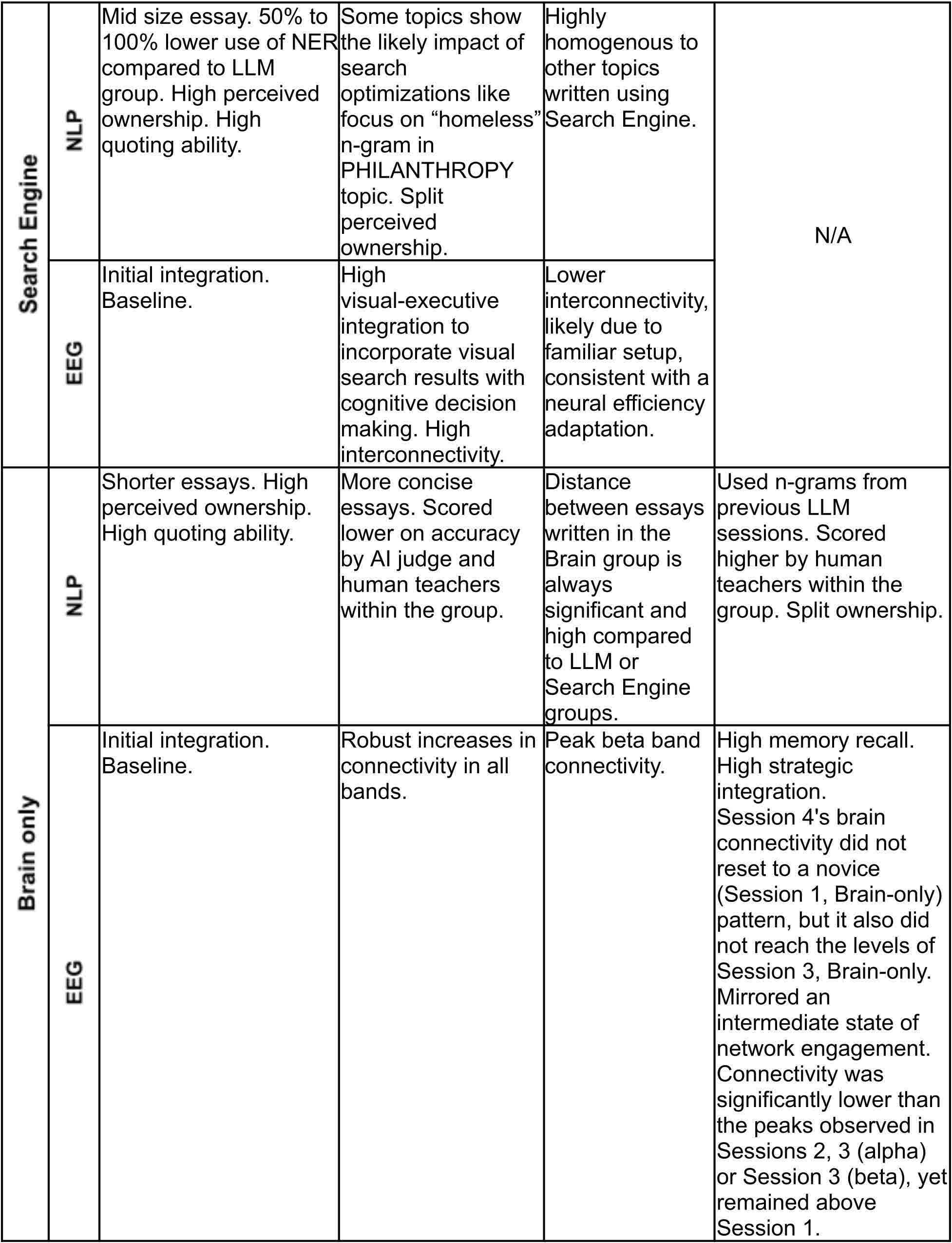
The newly printed paper explains that as members in an experiment wrote a collection of essays, digital mind monitoring revealed considerably weaker connections between areas of the mind in those that used giant language fashions (LLMs). This correlated with poorer reminiscence and extra spinoff output.
Three teams of members every wrote three essays: one group relied on an LLM, one other used search engines like google and yahoo, and the third labored with none exterior instruments. Then, the LLM and “brain-only” teams swapped members for a fourth essay. Though essays from the brain-only group weren’t all the time essentially the most correct, members in that group displayed considerably stronger neural connectivity, suggesting deeper psychological engagement.
Whereas essays from the LLM group acquired excessive marks from each human graders and AI judges, the writing tended to be extra homogeneous and adhered extra intently to the unique immediate. Contributors who used LLMs had been extra prone to copy and paste, edit their work much less, and battle to cite from their very own writing.
In the course of the ultimate session, LLM customers additionally had issue recalling info from earlier within the experiment. Their mind exercise had reset to a novice stage relating to the essay matters.
In the course of the ultimate session, LLM customers additionally had issue recalling info from earlier within the experiment. Their mind exercise had reset to a novice stage relating to the essay matters.
Though the brain-only group confirmed some decline in connectivity over time, it remained at an intermediate stage, and members might simply bear in mind earlier materials. Curiously, members who switched from the LLM group to the brain-only group confirmed elevated neural connectivity.
The group that used search engines like google and yahoo demonstrated low-to-intermediate mind connectivity. Their writing was additionally extremely homogeneous, however they had been higher capable of quote from their work, suggesting stronger reminiscence retention in comparison with LLM customers.
Total, the outcomes point out that any use of digital instruments impacts mind exercise, however search engines like google and yahoo require extra psychological engagement than generative AI.
These findings might have important implications for education, the place the usage of AI is becoming widespread. In many colleges, most college students now use instruments like ChatGPT to various levels when finishing assignments. Some generate solely outlines or matter concepts, whereas others use the assignments as prompts and submit the output with out a lot as studying it.
Academics and professors have additionally began using AI to grade assignments and attempt to detect the usage of AI, with various outcomes. The outcomes of the MIT research counsel that each teams would possibly endure cognitively, no matter how a lot or how little they depend on LLMs.